
Research Team
Chen Zhaomin, Zhan Junlin, Chen Hao, Yang Wu, Liu Zhenguo, Lu Weibing: National Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves, School of Information Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Purple Mountain Laboratories
Li Ya, He Hongjun: Future Research Institute, China Mobile Communications Corporation
Download Article
Chen Z M, Zhan J L, Chen H, et al. Robust textile-based spoof plasmonic frequencyscanning antenna for on-body loT applications. Sci China Inf Sci, 2024, 67(8): 182304

Significance of the study
Frequency beam-scanning antennas (FBSAs) have wide applications in the Internet of Things (IoT) due to their tunable beam, such as obstacle avoidance navigation, indoor positioning, remote vital sign monitoring, and wireless communication. However, when traditional copper-clad laminate (CCL)-based FBSAs are used in wearable devices, they can negatively impact user comfort. As next-generation human-computer interaction technologies increasingly move towards flexible devices, fabric-based flexible antennas, with their advantages of softness, breathability, and seamless integration with everyday clothing, are becoming an important choice for future body area network (BNB) communication applications.
However, in wearable scenarios, the structure of flexible fabric antennas often deforms, leading to changes or even deterioration in antenna performance, which in turn affects wireless communication performance. This is especially true for directional narrow-beam antennas like FBSAs, where structural deformation causes even more drastic changes in radiation performance. Furthermore, ensuring low specific absorption (SAR) is crucial for human safety in wearable communications. Therefore, achieving a compact FBSA with deformation resistance, low SAR, good environmental coverage, and comfortable wear has become a challenge in the fields of on-body obstacle avoidance navigation and wireless communication.
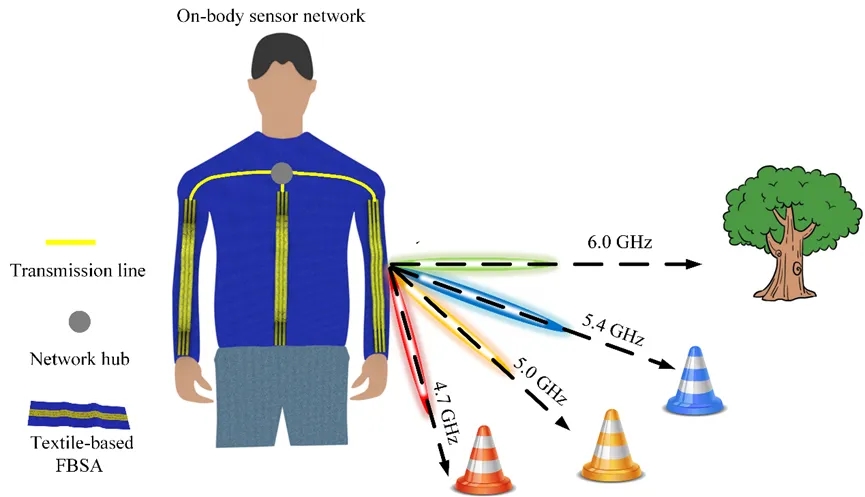
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of obstacle avoidance navigation concept on an anti-deformation fabric matrix FBSA body
This paper's work
To address the aforementioned issues, this paper proposes and designs a deformation-resistant fabric-based FBSA for measuring target angles and transmitting wireless signals to specific targets by adjusting the frequency. Figure 1 shows a conceptual schematic diagram of the proposed scheme.
Unlike traditional rigid or conformal surface-guided antennas (FBSAs), the antenna proposed in this paper uses aramid 3A (Nomex III-A) as the substrate and conductive fabric as the radiator, providing a low-profile and comfortable wearable technology solution. Compared to traditional methods that achieve forward frequency beam scanning through fundamental mode fast wave patterns, this paper utilizes periodic artificial surface plasmon polariton (SSPP) technology based on higher harmonic modes to achieve back-to-forward radiation, significantly expanding the coverage range of the radiation direction. To reduce antenna radiation to the human body and ensure wearer safety, an artificial magnetic conductor (AMC) plane is designed beneath the SSPP structure.
本文的主要贡献如下:
(1) 提出并探索了基于织物的抗变形人工等离子体频率扫描天线的概念。织物基材料的使用使得该天线能够无缝集成到衣物中,适用于体上可穿戴应用。
(2) 提出了一种新型SSPP单元设计。基于该单元的周期性调制天线(图2)在4.7–6.0 GHz频率范围内实现了70°的波束扫描角度范围,平均实现增益为13.15 dBi,该天线在应对人体活动引起的变形时表现出良好的鲁棒性。
(3) 通过引入AMC平面,有效降低了天线在与人体手臂模型贴合时的SAR值(0.113 W/kg),确保用户安全。同时,AMC平面将辐射波反射至上方空间,进一步提高了天线的辐射增益。
(4) 设计的SSPP单元确保了基于共面波导(CPW)的SSPP天线能够高效传输基模信号,展示了其作为紧凑型体上网络中多功能复合设备的潜力。
(5) 最后,通过无线通信质量实验,验证了所提天线在频率变化时能够测量目标角度,并实现向特定目标的无线信号传输。
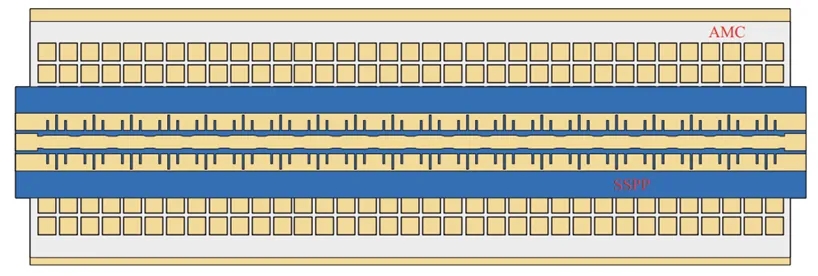
图2 抗变形的织物基FBSA
实验结果
为了验证所提出的设计,采用激光切割技术将Nomex III-A织物基板(介电常数2.605, 损耗正切角0.027, 厚度为0.5 mm)和导电织物(表面电阻为0.05 欧姆/平方)加工成预设图案。然后,使用切割-转移方法对原型进行处理。为了验证所提出的SSPP结构和天线在不同状态下S参数的鲁棒性,图3展示了测量SSPP结构和天线S参数的实验装置照片。
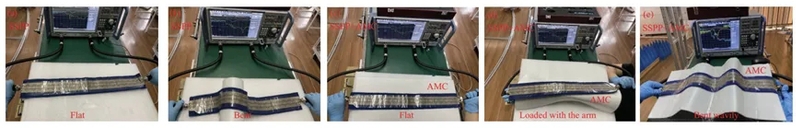
图3 测量SSPP结构和天线在不同状态下S参数的鲁棒性
图4显示了实测结果。其中图4(a)表明,所提出的SSPP结构在弯曲状态下,其S参数曲线几乎没有变化。图4(b)显示,所提出的天线对形变和人体手臂加载具有良好的鲁棒性。
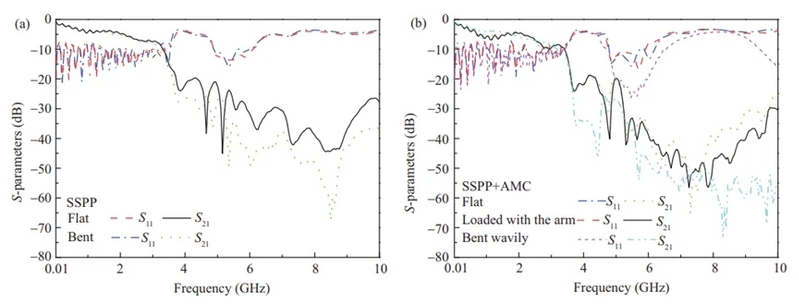
图4 S-参数实测结果:(a) 所提出的SSPP结构在平坦状态和弯曲状态下的表现;(b) 天线在平坦状态、加载手臂状态以及波状弯曲状态下的表现
此外,为了获取远场辐射性能,SSPP结构和天线还在暗室中进行了测量,结果展示在图5和图6中。加载AMC的SSPP结构有效抑制了AMC平面下方的波束辐射,将双波束辐射转换为单波束辐射。该SSPP结构在4.7至6.0 GHz的频率范围内展现了频率扫描辐射特性,实现了约70°的波束扫描角范围。
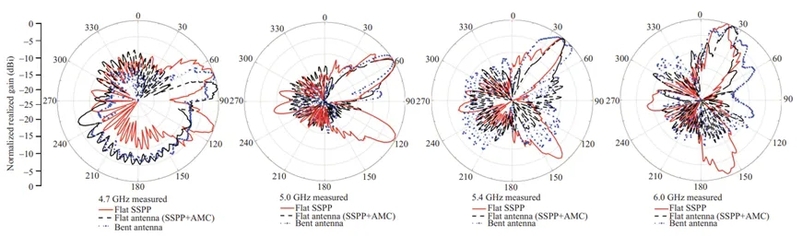
图5 对比了SSPP结构和平坦状态下的天线,以及波状弯曲状态下的天线在一些典型频率(如4.7 GHz、5.0 GHz、5.4 GHz和6.0 GHz)下的归一化实测辐射模式
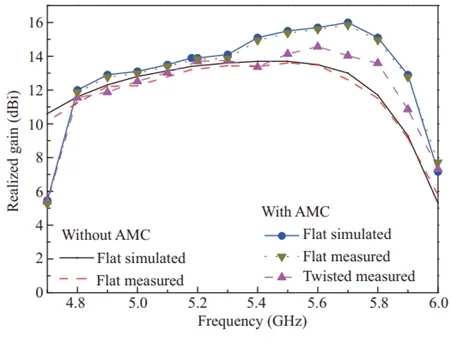
图6 SSPP结构与天线在不同状态下的实测与仿真的辐射增益
在弯曲场景下,天线在S参数、实现增益和辐射模式方面的表现表明其具有较高的鲁棒性,结构变形如波状弯曲几乎不会影响天线性能。值得注意的是,与S参数测量中考察的各种状态相比,我们的远场测量主要集中于研究天线在波状弯曲状态下的性能。这是因为所提出的天线专为体上手臂应用而设计的,而波状弯曲是手臂佩戴中最常见的情况。
为了验证所提出的天线在测量目标角度及通过频率变化实现向特定目标进行无线信号传输的能力,我们进行了实际的无线通信系统实验。实验使用了通用软件无线电外设(USRP)系统(来自武汉洛威的USRP N310),如图7所示。
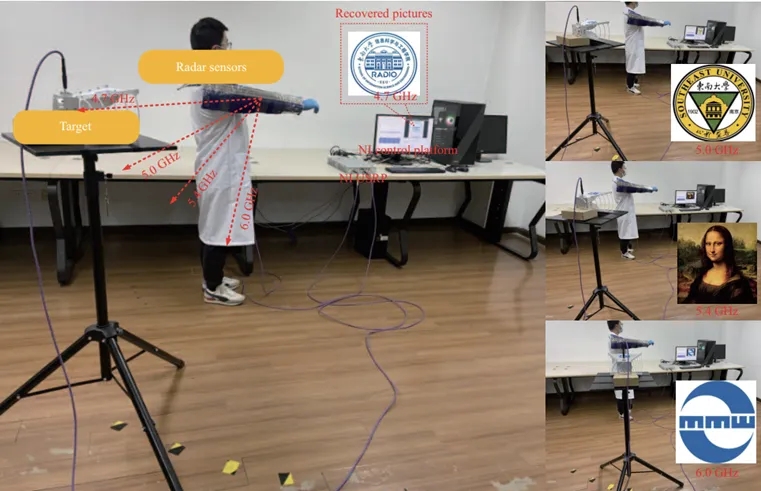

图7无线通信性能实验
实验中,将所提天线放置在人体手臂上,并连接到USRP系统的发射端口。作为测量目标,一只喇叭天线被放置在距离人体模型约140厘米的不同角度处,并随着操作频率进行调整,同时连接到USRP系统的接收端口。USRP系统的调制方案设置为二进制相移键控(BPSK)。实验环境建立后,在不同角度和频率变化下进行了无线图像通信实验。结果表明,所提出的天线能够有效测量目标角度,并在频率变化时实现对特定目标的无线信号传输,且未出现比特错误。这一表现展示了该天线在体上传感器网络和可穿戴无线通信系统领域的巨大潜力。



 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号